
|
|
ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY: The degree to which the naturally occurring resources of the planet (land, air, and water) are free of artificial impurities or waste products generated by human activity. Pollution is the primary nemesis of environmental quality. As pollution waste residuals are discharged into the environment, environmental quality declines. Like other economic notions, environmental quality is subjective in the sense that it affects the satisfaction of wants and needs.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL FACTOR COST, MONOPSONY: The opportunity cost incurred by a monopsony when using a given factor of production to produce a good or service. This is the total cost associated with the use of a particular resource or factor of production--it is the total cost of the factor. For monopsony, the price paid increases with the quantity purchased and total factor cost increases at an increasing rate. Total factor cost is predominately used in the analysis of the factor market. Two derivative factor cost measures are average factor cost and marginal factor cost. Total factor cost is the total opportunity cost incurred by a monopsony from the employment of a given resource. This measure of cost needs to be contrasted with a similar, better known term, total cost. Total cost is the cost of all factors of production, whereas total factor cost is the cost of using a specific factor. Total cost, as such, is the sum of the total factor cost of labor, the total factor cost of capital, and the total factor cost of all other inputs. Total factor cost can be represented in a table or as a curve. For a firm with no market control hiring inputs under perfect competition, the total factor cost curve is a straight line that emerges from the origin. For firms with market control, including monopsony, oligopsony, or monopsonistic competition, the total factor cost curve increases at an increasing rate. The shape of the total factor cost curve thus indicates the degree of market control possessed by the factor buyer. Whichever market structure is involved, total factor cost is calculated as the factor price times the quantity of the factor purchased, as illustrated by this equation: | total factor cost | = | factor price | x | factor quantity |
If the firm is hiring the factor in a perfectly competitive factor market, then the factor price is fixed or constant and total factor cost increases at a constant rate. If the firm is hiring the factor in an imperfectly competitive factor market, best illustrated by monopsony, then the factor price increases with larger factor quantities and the total factor cost increases at an increasing rate. For a market structure like monopsony that has some degree of market control and is a price maker rather than a price taker, total factor cost increases at an increasing rate. Although total factor cost is also calculated as price times quantity, market control means monopsony faces a positively-sloped supply curve. As such, the price received is not fixed, but depends on the quantity of the input bought. Total Factor Cost,
Monopsony | 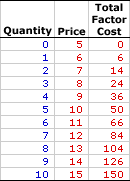 |
The table to the right summarizes the total factor cost received by a hypothetical firm, OmniKing Island Resort. This firm is the only employer of labor on a small tropical island. As the only employer of labor on the Island, OmniKing is a monopsony with extensive market control, and it faces a positively-sloped supply curve. To employ more workers, OmniKing must pay a higher price.Consider a few tidbits of information about total factor cost for a firm with market control, such as OmniKing Island Resort. - First, total factor cost is zero if OmniKing hires no labor. This makes sense. If nothing is bought, no factor cost is incurred.
- Second, the price changes with the quantity of output bought. OmniKing can hire 1 worker for $6. However, if it choses to hire 5 workers, then it must raise the price to $10.
- Third, as OmniKing hires more labor it pays more total factor cost.
- Fourth and last, the extra factor cost incurred from hiring more labor is not constant nor is it equal to the price. For example, the fifth worker adds a extra $14 to factor cost (the difference between $50 and $36) even though the price is $10.
Total Factor Cost Curve,
Monopsony | 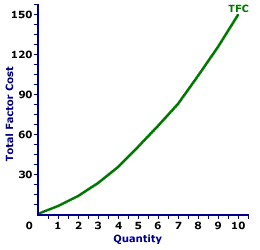 |
The total factor cost curve for the OmniKing Island Resort monopsony is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that OmniKing is a monopsony buyer of workers and thus faces a positively-sloped supply curve. Larger quantities of input can be had only with higher prices.The vertical axis measures total factor cost and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of input (workers). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 workers, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if OmniKing hires 1 worker (at $6 per worker), then it pays $6 of total factor cost. Alternatively, if it hires 10 workers (at $15 per worker), then it pays $150 of total factor cost. For OmniKing the total factor cost "curve" really is a "curve." The slope of this curve rises as more labor is hired. The changing slope of this curve is due to the changing price. Although this total factor cost curve is based on the employment activity of OmniKing Island Resort, a well-known monopsony firm, it applies to any buyer with market control. Monopsonistic competition and oligopsony firms that also face positively-sloped supply curves generate comparable total factor cost curves.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL FACTOR COST, MONOPSONY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 18, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs wanting to buy either super soft, super cuddly, stuffed animals or a large stuffed brown and white teddy bear. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Francis Bacon (1561-1626), a champion of the scientific method, died when he caught a severe cold while attempting to preserve a chicken by filling it with snow.
|

|
|
"Perhaps the most valuable result of all education is the ability to make yourself do the thing you have to do, when it ought to be done, whether you like it or not; it is the first lesson that ought to be learned; and however early a man's training begins, it is probably the last lesson that he learns thoroughly. " -- Thomas H. Huxley, Scientist
|

|
AIC
Akaike's Information Criterion
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


